The abbreviation MES comes from the English term Manufacturing Execution Systems. These are computer systems used in manufacturing plants to control and monitor production processes that lead to the conversion of raw materials into finished products and help production decision makers make important decisions or detect potential problems as soon as possible, leading to increased production efficiency. One of the main features of MES systems is that they work in real time.
MES systems form a link between enterprise information systems (most often represented by ERP - Enterprise Resource Planning) on the one hand and systems for production process and data collection (mostly SCADA - Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition) on the other. More can be found in the article - MES / MOM: Integration with surrounding systems.
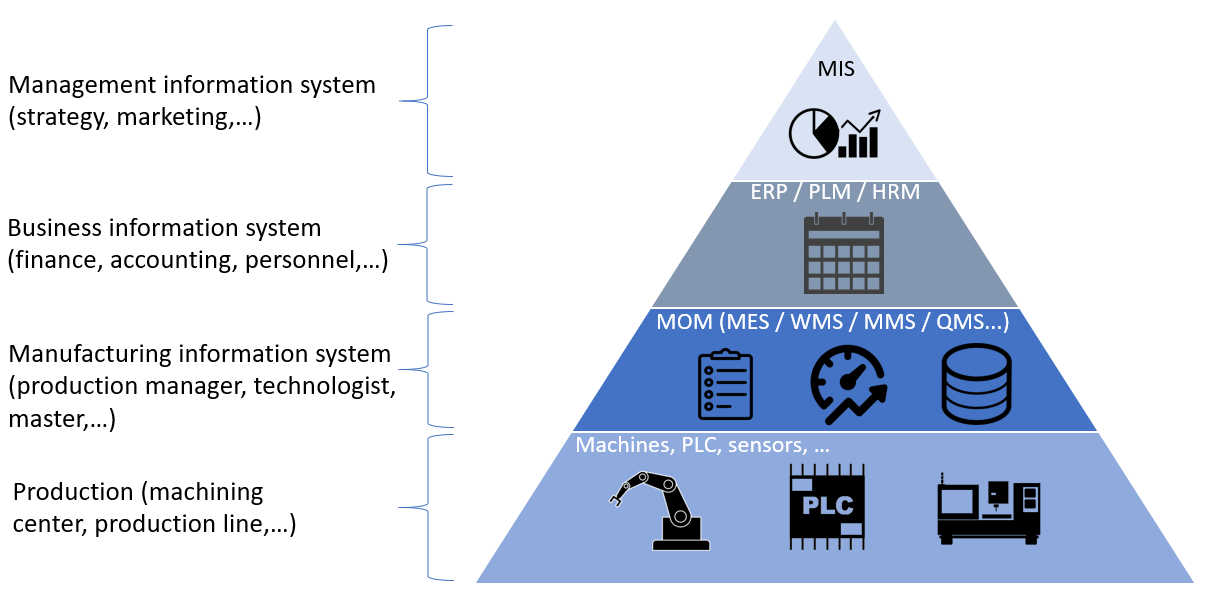
MES systems are intertwined in many areas (see - MES system – core functions), from production process management, production planning and scheduling, production evaluation, downtime management, quality process management, material traceability, data collection, performance analysis, such as evaluation of overall equipment efficiency (more information on OEE can be found in the OEE article and derived TEEP, PEE, OAE, OPE, OFE, OTE and CTE indicators).
MES systems help create faultless production processes and help create a consistent view of production data. Other benefits of a successfully implemented MES system are:
- traceability of production,
- ensuring accurate production data,
- reduction of downtime, nonconforming production, shortening of setting times,
- increase overall equipment efficiency (OEE)
- reduction of inventory,
- introduction of paperless production,
- possibility of accurate economic evaluation of production and others.

 English (UK)
English (UK)  Česky (CS)
Česky (CS)